VSAQ for Chapter 11 From Barter to Money Class 7 Social Science NCERT
Important Questions1
Q1: What was the barter system?
Answer
The barter system was the exchange of goods and services without using money.
VSAQ
2
Q2: What was a major problem with the barter system?
Answer
A major problem with the barter system was the double coincidence of wants, meaning both parties had to want what the other offered.
VSAQ
3
Q3: What is money?
Answer
Money is a common tool used for buying and selling goods and services.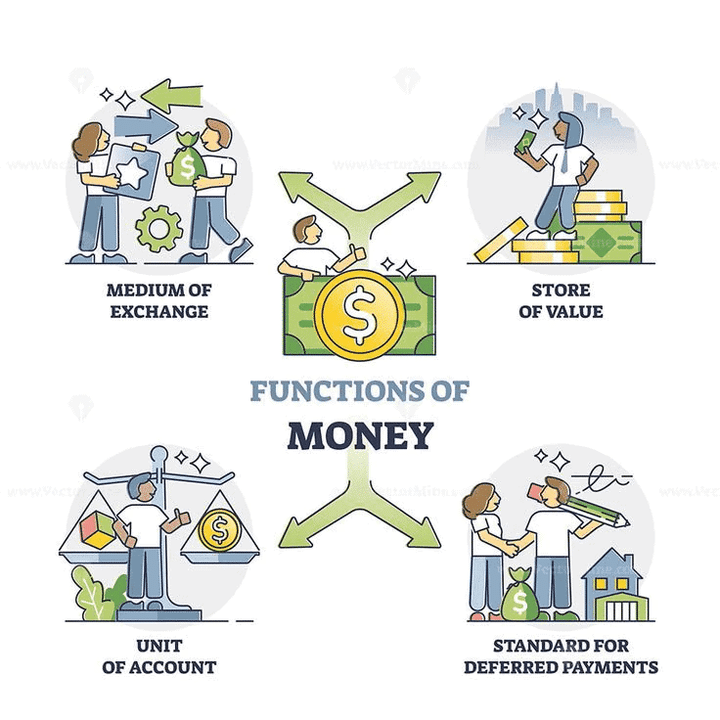
Functions of Money
VSAQ
4
Q4: Who is John Maynard Keynes?
Answer
John Maynard Keynes was an economist who said that money connects the present to the future by helping us save and spend later.
VSAQ
5
Q5: Why did the barter system become inefficient?
Answer
The barter system became inefficient due to problems like the difficulty of finding someone who wanted what you offered and the inability to divide goods like cattle.
VSAQ
6
Q6: How does money solve the problems of the barter system?
Answer
Money solves these problems by being portable, divisible, durable, and a standard measure of value.
VSAQ
7
Q7: What is meant by "double coincidence of wants"?
Answer
Double coincidence of wants means both parties in a trade must want what the other offers, which is rare and difficult.
VSAQ
8
Q8: How is money different from goods in the barter system?
Answer
Money is portable, divisible, and accepted by everyone, unlike goods which may not be easily traded or split.
VSAQ
9
Q9: What is the importance of the medium of exchange function of money?
Answer
The medium of exchange function allows money to be used universally for buying and selling goods and services.
VSAQ
10
Q10: How does money serve as a store of value?
Answer
Money serves as a store of value by allowing people to save it and use it later, unlike perishable goods like wheat.
VSAQ
11
Q11: What does "common denomination" mean in the context of money?
Answer
Common denomination means money is used to measure the value of goods, making it easy to compare prices.
VSAQ
12
Q12: What is a "standard of deferred payment"?
Answer
A standard of deferred payment means money can be used to make payments later, as in buying goods on credit.
VSAQ
13
Q13: What are "cowrie shells" in relation to money?
Answer
Cowrie shells were used as money in ancient times in different parts of the world, including India.
Cowrie Shells
VSAQ
14
Q14: What are "Rai stones"?
Answer
Rai stones were large stone discs used as money in Micronesia, symbolizing wealth.
VSAQ
15
Q15: Why were coins important in the history of money?
Answer
Coins were important because they provided a standardized, easily recognizable form of money made from precious metals like gold and silver.
VSAQ
16
Q16: What were "kārshāpanas" in ancient India?
Answer
Kārshāpanas were ancient Indian coins made from precious metals, used for transactions in the Mauryan Empire.
VSAQ
17
Q17: What was the role of the Roman coins in India?
Answer
Roman coins found in Tamil Nadu and Kerala show that India had strong maritime trade connections with the Roman Empire.
VSAQ
18
Q18: When was paper currency introduced in India?
Answer
Paper currency was introduced in India in the late 18th century by banks like the Bank of Bengal and Bank of Bombay.
VSAQ
19
Q19: What are modern banknotes in India made of?
Answer
Modern Indian banknotes are made of cotton paper, with special features like raised marks for the visually impaired.
VSAQ
20
Q20: What is the ₹ symbol, and who designed it?
Answer
The ₹ symbol represents the Indian Rupee and was designed by Udaya Kumar in 2010, combining Devanagari and Roman characters.
VSAQ
21
Q21: What is digital money?
Answer
Digital money refers to intangible money that exists electronically, such as through mobile payments or bank transfers.
VSAQ
22
Q22: What are QR codes used for in modern transactions?
Answer
QR codes are used for digital payments, allowing customers to pay directly from their bank accounts using their phones.
VSAQ
23
Q23: What is UPI?
Answer
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a digital payment system that enables instant transfer of money between bank accounts using smartphones.
VSAQ
24
Q24: How did the introduction of paper currency benefit trade?
Answer
Paper currency made it easier to carry large sums of money for trade and reduced the need to transport heavy coins.
VSAQ
25
Q25: What is one example of a modern barter system in India?
Answer
The Junbeel Mela in Assam is a modern example where people exchange roots, vegetables, and handmade goods for food items like rice cakes.
VSAQ
26
Q26: What was the primary problem with the barter system?
Answer
The main problem was the double coincidence of wants.
VSAQ
27
Q27: What does "money as a store of value" mean?
Answer
Money can be saved and used later, unlike perishable goods.
VSAQ
28
Q28: How did the invention of money help in trade?
Answer
Money made trade easier by solving the issues of portability, divisibility, and value measurement.
VSAQ
29
Q29: What is the modern equivalent of money used in daily transactions?
Answer
Modern money includes coins, notes, and digital payments like UPI.
VSAQ
30
Q30: What does "durability" mean in the context of money?
Answer
Money can last for a long time without spoiling, unlike perishable goods in the barter system.
Paper Currency
VSAQ