SAQ for Chapter 11 From Barter to Money Class 7 Social Science NCERT
Important Questions1
Q1: What problems did the barter system have that led to the need for money?
Answer
The barter system had issues like double coincidence of wants, where both parties needed to have what the other wanted. It also lacked a common standard of value, and goods like cattle were not portable or divisible, making trade slow and inefficient.
Barter System
SAQ
2
How did the introduction of money simplify trade compared to the barter system?
Answer
Money simplified trade by providing a portable, divisible, and universally accepted medium of exchange. It allowed for easier transactions, and people could store value and make future payments, overcoming the limitations of the barter system.
SAQ
3
Q3: What is the role of money as a store of value?
Answer
Money acts as a store of value by allowing individuals to save it for future use. Unlike perishable goods like wheat, money does not lose its value quickly, making it easy to save for future purchases or investments.
SAQ
4
Q4: How does the common denomination function of money help in trade?
Answer
The common denomination function of money helps by allowing goods of different values to be compared and priced in a standard way. This makes it easier for people to understand the worth of various items and conduct transactions efficiently.
SAQ
5
Q5: Why did early societies use items like cowrie shells and Rai stones as money?
Answer
Early societies used items like cowrie shells and Rai stones as money because they were valuable, durable, and could be easily traded. These items were widely accepted in their respective regions as a form of exchange.
SAQ
6
Q6: How did the advent of coins change trade in ancient India?
Answer
The advent of coins in ancient India made trade more efficient by providing a standardized, portable, and durable form of money. Coins made from metals like gold, silver, and copper were easy to carry and were accepted across regions, promoting wider trade networks.
SAQ
7
Q7: What was the significance of the introduction of paper currency in India?
Answer
The introduction of paper currency in India provided a more convenient way to handle large sums of money, especially for higher denominations. It made trade easier and reduced the need to carry heavy coins, facilitating smoother transactions.
SAQ
8
Q8: How did the design of modern Indian currency notes evolve?
Answer
Modern Indian currency notes feature cultural motifs, symbols, and security features like raised marks for the visually impaired. These notes are made of durable cotton paper and are designed to prevent counterfeiting and to reflect India’s heritage.
Paper Currency
SAQ
9
Q9: How does digital money work, and how has it impacted modern transactions?
Answer
Digital money works through electronic systems like mobile payments, bank transfers, and online banking. It has made transactions faster, easier, and more accessible, reducing the need for physical money and increasing convenience for users.
SAQ
10
Q10: What is UPI, and how does it simplify payments?
Answer
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a digital payment system that allows users to transfer money instantly between bank accounts using their mobile phones. It simplifies payments by linking multiple bank accounts to a single app and facilitates easy transactions.
SAQ
11
Q11: How do QR codes facilitate digital payments in modern commerce?
Answer
QR codes facilitate digital payments by providing a quick and secure way to transfer money from one person’s bank account to another. By scanning the code with a smartphone, payments can be made instantly, making transactions more efficient.
SAQ
12
Q12: What were the limitations of the barter system that money helped overcome?
Answer
The barter system had limitations such as the double coincidence of wants, where both parties needed to have what the other wanted, and issues with portability, divisibility, and durability. Money solved these problems by offering a universally accepted, portable, divisible, and durable means of trade.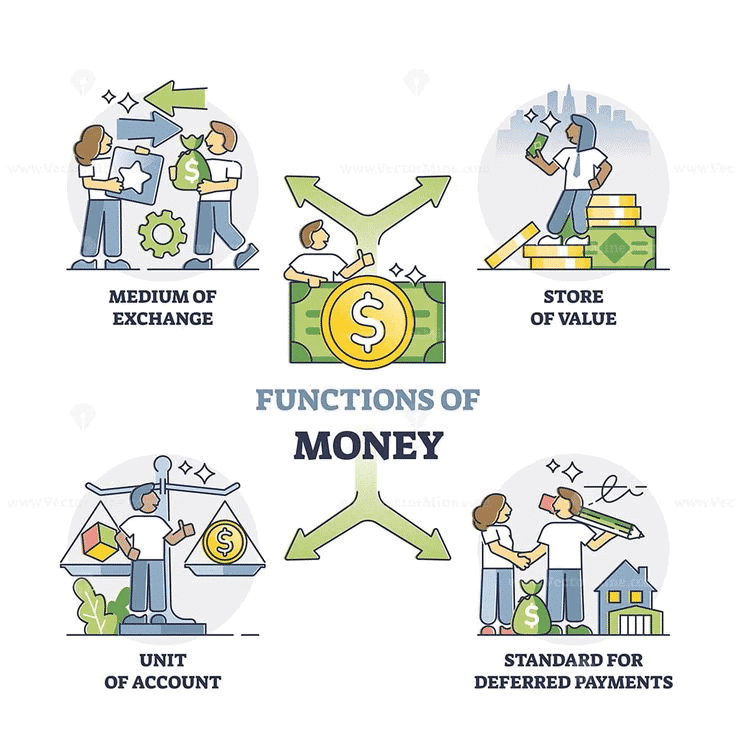
SAQ
13
Q13: Why was the barter system not effective for long-distance trade?
Answer
The barter system was ineffective for long-distance trade because goods like cattle were hard to transport, and the double coincidence of wants was difficult to find.
SAQ
14
Q14: Explain the difference between the barter system and money.
Answer
The barter system required a mutual need for goods, while money is a common, portable, and divisible medium of exchange, making trade more efficient.
SAQ
15
Q15: What was the first form of paper currency used in India?
Answer
Paper currency was introduced in India in the late 18th century by banks like the Bank of Bengal and Bank of Bombay.
SAQ
16
Q16: How did money evolve from coins to digital money?
Answer
Money evolved from coins made of precious metals to paper currency and now to digital money like UPI and mobile payments for easier transactions.
SAQ
17
Q17: How did John Maynard Keynes describe the role of money?
Answer
John Maynard Keynes described money as a means to connect the present with the future, helping people save and spend later.
SAQ