SAQ for Chapter 6 The Age of Reorganization Class 7 Social Science NCERT
Important Questions1
Q1: How did the Śhunga dynasty come to power?
Answer
The Śhunga dynasty was founded by Puṣhyamitra Śhunga after he assassinated the last Maurya emperor in 185 BCE. Puṣhyamitra, a commander in the Maurya army, seized power and began ruling parts of northern and central India.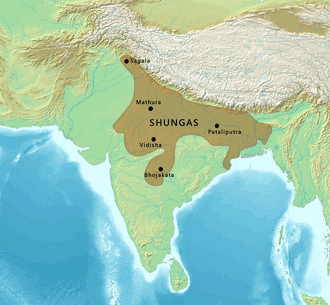
Shunga Dynasty
SAQ
2
Q2: What impact did the Śhunga Empire have on art and culture?
Answer
The Śhunga Empire supported literature, art, and architecture, leading to significant cultural contributions. They added carvings to the Bharhut Stūpa and promoted Sanskrit as a language for philosophy and literature.
SAQ
3
Q3: How did the Sātavāhanas contribute to trade and the economy?
Answer
The Sātavāhanas promoted trade by controlling important trade routes and engaging in maritime trade with the Roman Empire. Their economy thrived due to agriculture, the fertile river systems, and the wealth generated from trade.
SAQ
4
Q4: What role did the Naneghat Caves play in trade during the Sātavāhana period?
Answer
The Naneghat Caves, located along trade routes, were used for collecting tolls from traders. They also served as resting places for traders on their journey through the region.
Naneghat Cave Near Pune
SAQ
5
Q5: How did the kingdoms of south India, like the Cheras, Cholas, and Pāṇḍyas, promote trade?
Answer
The south Indian kingdoms promoted trade by exporting goods such as spices, timber, ivory, and pearls. They maintained strong trade connections with the Roman Empire and other regions, boosting their economies.
SAQ
6
Q6: What does the Silappadikāram tell us about the Chola, Pāṇḍya, and Chera kingdoms?
Answer
The Silappadikāram, an epic from the Sangam Age, highlights the values of justice and the responsibilities of rulers. It showcases life in the Chola, Pāṇḍya, and Chera kingdoms, including their cultural practices, justice systems, and social norms.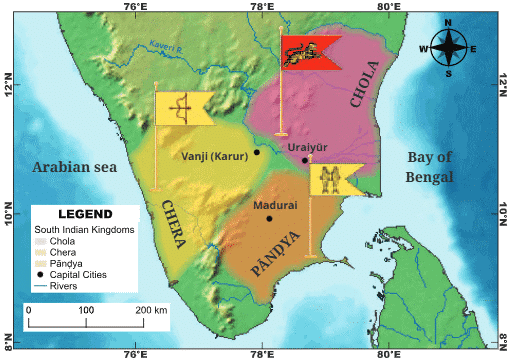
Chera, Chola, Pandya
SAQ
7
Q7: How did King Karikāla contribute to the agricultural development of the Chola kingdom?
Answer
King Karikāla built the Kallanai (Grand Anicut), a water diversion system on the Kāveri River, to irrigate the delta. This allowed the Chola kingdom to become the “rice bowl of the South” and greatly boosted agricultural productivity.
SAQ
8
Q8: What was the significance of the Chera kingdom in the context of trade and culture?
Answer
The Chera kingdom was important for its role in trading spices, timber, ivory, and pearls. It also supported Tamil literature, including Sangam poetry, and was a center for cultural exchange with other regions.
SAQ
9
Q9: How did the Pāṇḍyas contribute to India’s trade relations with other regions?
Answer
The Pāṇḍyas were key players in the pearl trade, exchanging pearls and other goods with the Greeks and Romans. They also maintained a strong naval presence, which helped establish their trade networks.
SAQ
10
Q10: What was the role of Khāravela in promoting Jainism?
Answer
Khāravela, the ruler of the Chedi dynasty, promoted Jainism and built the Udayagiri-Khandagiri Caves as shelters for Jain monks. He was known for his religious tolerance and support for all schools of thought.
SAQ
11
Q11: What is the significance of the Indo-Greek rulers in India’s cultural history?
Answer
The Indo-Greek rulers introduced Greek art and culture to India, blending it with Indian traditions. They promoted Hellenistic styles in art, coinage, and governance, which influenced later Indian artistic traditions.
SAQ
12
Q12: How did the Kuṣhāṇas impact India’s cultural and trade connections?
Answer
The Kuṣhāṇas promoted trade along the Silk Route, linking India to Central Asia and the West. They also supported the spread of Buddhism and their art, such as the Gandhara and Mathura styles, combined Greek and Indian influences.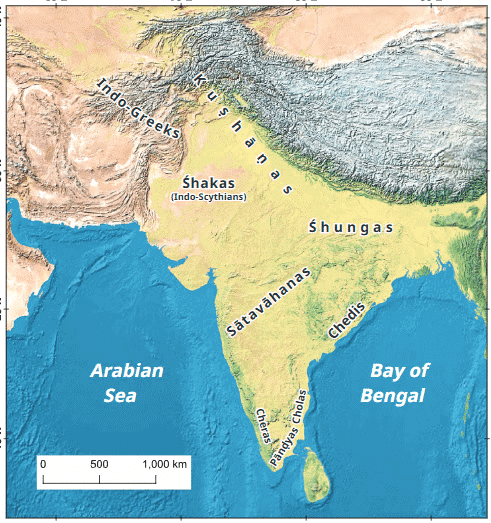
Prominent Dynasties of India during Reorganisation
SAQ
13
Q13: How did the Śhunga Empire influence Indian culture?
Answer
The Śhunga Empire revived Vedic rituals, promoted Sanskrit literature, and contributed to art by building the Bharhut Stūpa with beautiful carvings.
SAQ
14
Q14: What role did trade play in the Sātavāhana Empire?
Answer
The Sātavāhanas thrived on trade, especially maritime trade, importing goods like glass and perfumes while exporting spices, textiles, and ivory.
SAQ
15
Q15: How did the Indo-Greek rulers blend their culture with Indian traditions?
Answer
The Indo-Greeks adopted Indian culture, blending Greek and Indian artistic styles and religious practices, as seen in their coins and sculptures.
SAQ
16
Q16: Why did the Sātavāhanas support multiple religions?
Answer
The Sātavāhanas, while supporting Vedic rituals, allowed Jains, Buddhists, and other groups to thrive by providing them with land and patronage.
SAQ
17
Q17: What was the significance of the Kalinga War in Ashoka’s life?
Answer
The Kalinga War led Ashoka to embrace Buddhism and non-violence, promoting peace and moral governance through his edicts.
SAQ