LAQ for Chapter 4 The World of Metals and Non-metals Class 7 Science NCERT
Important Questions1
Q1: Describe the physical properties of metals and how they differ from non-metals.
Answer
Metals generally exhibit properties like metallic lustre, malleability, ductility, sonority, and high conductivity of heat and electricity. Non-metals, on the other hand, are generally non-lustrous, brittle, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. Metals can be hammered into sheets (malleable) and drawn into wires (ductile), whereas non-metals lack these properties. Non-metals also form acidic oxides when they react with oxygen, while metals typically form basic oxides.2
Q2: How does the reaction of metals and non-metals with oxygen differ?
Answer
Metals generally react with oxygen to form basic metal oxides, such as iron oxide (rust), which is alkaline in nature. Non-metals, on the other hand, form acidic oxides when they react with oxygen, such as sulfur dioxide, which forms sulfurous acid when dissolved in water. This difference in reactions is key to understanding the nature of oxides formed by metals and non-metals.3
Q3: Explain the process of rusting and how it can be prevented.
Answer
Rusting is the process where iron reacts with oxygen and water to form iron oxide (rust), which causes the iron to deteriorate. Rusting can be prevented by methods such as painting, oiling, greasing, or applying a protective layer of zinc (galvanization). These methods protect the iron from direct exposure to air and water, thus preventing corrosion.
4
Q4: What are the applications of metals in daily life?
Answer
Metals have numerous applications in daily life due to their distinct properties. For instance, metals like copper and aluminium are used for electrical wiring due to their excellent conductivity. Iron and steel are used in construction and making tools due to their strength and malleability. Precious metals like gold and silver are used in jewelry, while aluminium is used in food packaging materials due to its malleability and low cost. Metals are also used in the manufacturing of machinery, vehicles, and electronics.5
Q5: Discuss the uses of non-metals in everyday life.
Answer
Non-metals like oxygen are essential for respiration, making them crucial for life. Nitrogen is used in fertilizers to enhance plant growth. Carbon is an important element in organic molecules and fuels. Chlorine is used in water purification, while iodine is used as an antiseptic for wounds. Non-metals are also found in medicines, food preservation, and industrial applications like rubber manufacturing and water treatment.6
Q6: Explain the properties of metals and non-metals and how they differ.
Answer
Metals are generally lustrous, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. They form basic oxides when they react with oxygen. Non-metals, on the other hand, are usually non-lustrous, brittle, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. They form acidic oxides when they react with oxygen and do not have the properties of malleability and ductility.7
Q7: Why are gold and silver used in jewellery, and why are only a few metals suitable for this purpose?
Answer
Gold and silver are highly malleable and ductile, allowing them to be shaped into intricate designs and thin sheets. They are also resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for jewellery. However, not all metals possess these qualities, as some are too hard or reactive to be used for jewellery.8
Q8: Describe the process of rusting and the methods used to prevent it.
Answer
Rusting is the process where iron reacts with oxygen and water, forming brown deposits on its surface. To prevent rusting, methods such as painting, oiling, greasing, or applying a protective layer of zinc (galvanisation) are used. These methods prevent exposure to air and water, which are necessary for rust formation.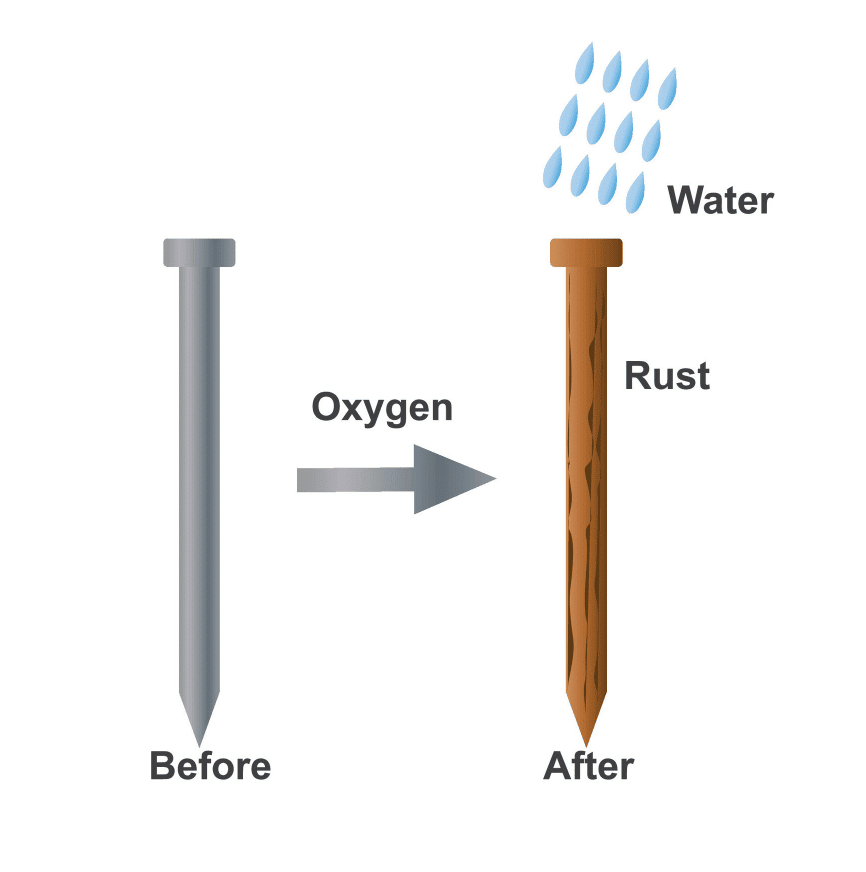
9
Q9: How do the properties of metals and non-metals influence their uses in everyday life?
Answer
The properties of metals, such as conductivity, malleability, and ductility, make them useful in applications like electrical wiring, construction, and manufacturing tools. Non-metals, though poor conductors, are essential in biological processes, like oxygen for respiration and carbon for life forms, and are also used in the production of fertilizers and water purification.10
Q10: What is the significance of the Iron Pillar of Delhi, and what does it tell us about ancient Indian metallurgy?
Answer
The Iron Pillar of Delhi is a remarkable example of ancient Indian metallurgy. Despite facing exposure to wind, rain, and intense weather for over 1600 years, it shows very little rust. This indicates advanced techniques in metalworking that allowed for resistance to rusting, demonstrating the high level of skill in metallurgy in ancient India.