LAQ for Chapter 12 Earth, Moon, and the Sun Class 7 Science NCERT
Important Questions1
Q1: Explain the process of Earth’s rotation and how it affects the day-night cycle.
Answer
The Earth rotates on its axis, which is an imaginary line running from the North Pole to the South Pole. This rotation occurs in an anti-clockwise direction when viewed from above the North Pole. As the Earth rotates, different parts of the planet move into sunlight, experiencing daytime, while the opposite side is in darkness, experiencing night. This rotation is the primary cause of the cycle of day and night, with each full rotation taking approximately 24 hours.
LAQ
2
Q2: Describe the difference between Earth’s rotation and revolution.
Answer
Earth’s rotation refers to its spinning on its axis, taking about 24 hours to complete one rotation. This causes day and night. On the other hand, Earth's revolution is the motion of the Earth around the Sun, taking approximately 365 days and 6 hours to complete one full orbit. The revolution is responsible for the changing seasons on Earth.
LAQ
3
Q3: How do the Earth’s rotation and revolution contribute to the changing seasons?
Answer
The Earth’s rotation gives rise to the day-night cycle, but it is the revolution that causes the changing seasons. Due to the Earth’s axial tilt, different hemispheres receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it experiences summer, while the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter. In December, the tilt reverses, and the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter, while the Southern Hemisphere experiences summer. This axial tilt and Earth’s orbit around the Sun are the main factors contributing to the seasonal changes.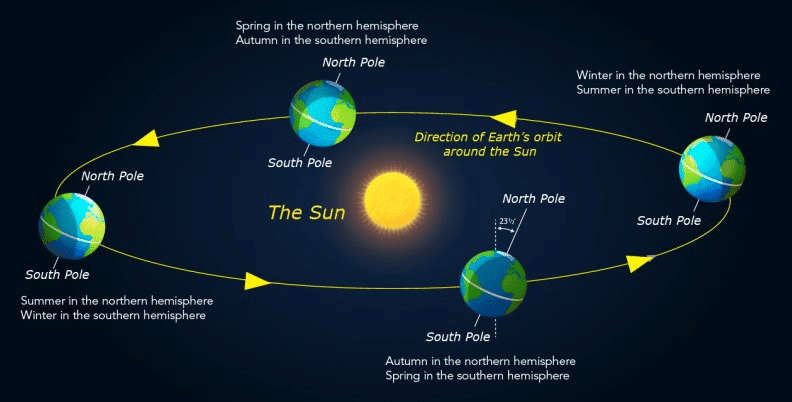
LAQ
4
Q4: What is the geometry behind a solar eclipse? Explain how it occurs.
Answer
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth, blocking the Sun’s light from reaching the Earth. The Moon casts a shadow on Earth, which can either be a total or partial eclipse, depending on the alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. In a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely covers the Sun, and the sky becomes dark during the day. A partial solar eclipse occurs when only a part of the Sun is blocked. This event is brief, as the Moon’s shadow moves across the Earth’s surface due to the Earth's rotation.
LAQ
5
Q5: Discuss the safety precautions that should be followed while observing a solar eclipse.
Answer
It is crucial not to look directly at a solar eclipse with the naked eye, as it can cause serious eye damage. Special eclipse glasses that meet safety standards should be used for direct viewing. Alternatively, indirect methods, such as using a mirror to project the Sun’s image onto a screen, can also be used. Never observe a solar eclipse through regular sunglasses, binoculars, or telescopes unless they are equipped with proper solar filters. It is also recommended to participate in organized eclipse viewing events where experts provide the necessary equipment and safety instructions.
LAQ
6
Q6: Explain the phenomenon of day and night on Earth.
Answer
Day and night occur because the Earth rotates on its axis. As the Earth rotates, one half of the planet faces the Sun, experiencing daylight, while the other half is in darkness, experiencing nighttime. This rotation takes approximately 24 hours, causing a complete cycle of day and night.
LAQ
7
Q7: Describe the process of a solar eclipse and how it occurs.
Answer
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light. The Moon’s shadow falls on the Earth, causing a temporary period of darkness. Depending on the alignment, it can be a total solar eclipse, where the Sun is completely blocked, or a partial solar eclipse, where only a part of the Sun is obscured.
LAQ
8
Q8: What is the effect of the Earth’s tilt on the seasons?
Answer
The tilt of the Earth’s axis, combined with its revolution around the Sun, causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight at different times of the year. This variation in sunlight results in the four seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter, each with different lengths of days and nights.
LAQ
9
Q9: How does the Earth’s rotation lead to the apparent motion of stars in the sky?
Answer
As the Earth rotates on its axis, the stars appear to move across the sky. In the Northern Hemisphere, stars appear to move in a circular path around the North Star. This motion is due to the Earth’s rotation, which gives the illusion that the stars are moving from east to west.
LAQ
10
Q10: What are the differences between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse?
Answer
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. Solar eclipses are visible only in small areas, while lunar eclipses can be seen from a much larger part of the Earth.
LAQ