Extra Question Answer for Chapter 2 Class 6 Science
Important Questions1
(i) The __________ is the natural environment where a plant or animal lives.
(ii) __________ are plants with weak stems that need support to grow.
(iii) The variety and differences found among living things in a particular area is known as __________.
(iv) __________ are animals that can live both on land and in water.
(v) __________ plants have hard, woody stems.
(ii) __________ are plants with weak stems that need support to grow.
(iii) The variety and differences found among living things in a particular area is known as __________.
(iv) __________ are animals that can live both on land and in water.
(v) __________ plants have hard, woody stems.
Answer
(i) habitat(ii) Climbers
(iii) diversity
(iv) Amphibians
(v) Trees
Fill in the Blanks
2
(i) Rhododendrons in the Nilgiris are typically shorter with smaller leaves.
(ii) All plants with parallel venation have dicotyledonous seeds.
(iii) Adaptations are characteristics that help organisms survive in their specific environment.
(iv) Desert plants like cacti have large, broad leaves to capture water.
(v) Mountain goats are adapted to live in the ocean.
(ii) All plants with parallel venation have dicotyledonous seeds.
(iii) Adaptations are characteristics that help organisms survive in their specific environment.
(iv) Desert plants like cacti have large, broad leaves to capture water.
(v) Mountain goats are adapted to live in the ocean.
Answer
(i) True(ii) False
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) False
True or False
3
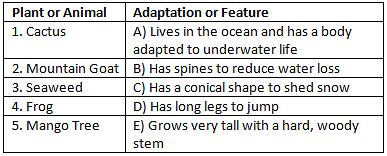
Answer
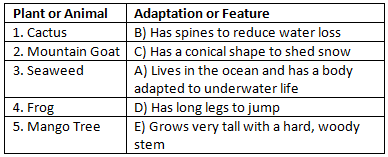
Match the Following
4
What does diversity in plants and animals mean?
Answer
Diversity refers to the variety and differences among living things in an area.
Very short
5
Name one characteristic that differentiates trees from shrubs.
Answer
Trees are taller and have branches that start higher up the stem compared to shrubs.
Very short
6
What type of stem do herbs typically have?
Answer
Herbs usually have soft and green stems.
Very short
7
How can leaves differ among plants?
Answer
Leaves can differ in shape, size, and arrangement on the stem.
Very short
8
What is a common example of a plant with a taproot?
Answer
The mustard plant is a common example of a plant with a taproot.
Very short
9
What type of root system do grasses have?
Answer
Grasses have a fibrous root system.
Very short
10
How do birds typically move?
Answer
Birds typically move by flying using their wings.
Very short
11
What is one way to group plants?
Answer
Plants can be grouped based on their height, such as trees, shrubs, and herbs.
Very short
12
Give an example of a plant with reticulate venation.
Answer
The hibiscus plant is an example of a plant with reticulate venation.
Very short
13
What is biodiversity?
Answer
Biodiversity is the variety of different plants, animals, and organisms in a region.
Very short
14
What is the purpose of grouping animals?
Answer
To study their behavior, characteristics, and shared features.
Very short
15
Name an animal that can fly.
Answer
Bird.
Very short
16
What adaptation helps camels survive in the desert?
Answer
Humps that store fat for energy.
Very short
17
Which tree is adapted to snowy mountain conditions?
Answer
Deodar tree.
Very short
18
Identify a plant that thrives in the ocean.
Answer
Seaweed.
Very short
19
What is a habitat?
Answer
The natural environment where a plant or animal lives.
Very short
20
Give an example of an aquatic habitat.
Answer
Ocean.
Very short
21
What type of animal can live both on land and in water?
Answer
Amphibian.
Very short
22
Why is protecting biodiversity important?
Answer
It ensures all living things can thrive.
Very short
23
Name one way to help protect the environment.
Answer
Planting trees.
Very short
24
What is biodiversity?
Answer
Biodiversity refers to the variety of all forms of life on Earth, including different plants, animals, microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
Short Answer
25
What is a habitat?
Answer
A habitat is the natural environment where a plant or animal lives and obtains its food, water, shelter, and other survival needs.
Short Answer
26
What is adaptation?
Answer
The change in specific features or certain habits, which enables a plant or an animal to live in its surroundings is called adaptation.
Short Answer
27
How do plants adapt to survive in deserts?
Answer
Plants in deserts often have fleshy stems to store water and may have spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss.
Short Answer
28
What is the importance of grouping plants and animals?
Answer
Grouping makes it easier to understand and study plants and animals on the basis of their similarities and differences.
Short Answer
29
What are biotic components?
Answer
The living things such as plants and animals in a habitat are its biotic components.
Short Answer
30
Explain abiotic components.
Answer
Various non-living things such as rocks, soil, air and water in a habitat constitute its abiotic components.
Short Answer
31
What are fibrous roots?
Answer
Fibrous roots are a type of root system where many thin roots spread out from the base of the stem, common in plants with parallel venation.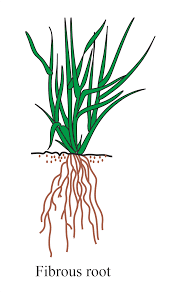
Short Answer
32
Give an example of an aquatic habitat and an organism that lives there.
Answer
An example of an aquatic habitat is a pond, and a fish is an organism that lives there.
Short Answer
33
What are aquatic habitats?
Answer
Habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitat.
Short Answer
34
What is the difference between terrestrial and aquatic habitats?
Answer
errestrial habitats are those found on land, while aquatic habitats are found in water bodies like ponds, lakes, and oceans.
Short Answer
35
What type of venation is found in the leaves of monocots?
Answer
Monocots typically have parallel venation in their leaves. In monocotyledonous (monocot) plants, the veins in the leaves run parallel to each other, forming a pattern where the veins are aligned along the length of the leaf. This is in contrast to dicotyledonous (dicot) plants, which typically have a reticulate (net-like) venation pattern where the veins form a branching network.
Long Answer
36
What are the specific features present in a deer that helps it to detect the presence of predators like lion?
Answer
The specific features present in a deer that helps it to detect the presence of predators like lion are:(a) Long ears to hear movement of predators.
(b) Eyes on the sides of its head which allow it to look in all directions.
Long Answer
37
How is cactus adapted to survive in a desert?
Answer
Cactus is adapted to survive in a desert as it has:• No leaves or spiny leaves to prevent water loss through transpiration.
• It stores water in its fleshy stems.
• Its roots go very deep into the soil for absorbing water.
Long Answer
38
How do amphibians differ from other animals in terms of habitat?
Answer
Amphibians can live both on land and in water, unlike most other animals that are specialized for one type of habitat.
Long Answer
39
What are herbs?
Answer
The small plants with soft tender, green, short stem are called herbs. Herbs hardly attain height more than 1.5 metres. Their stems are not woody and can be bent. A herb may or may not have branches, e.g., tomato, mint, paddy, etc.
Long Answer
40
What are climbers and creepers? Give some examples.
Answer
In some plants like grape vines, money plant, bean stalk, gourd plants, etc., the stem is so weak that it cannot hold it straight. They either stand up with some support or they just spread on the ground. The ones which climb up are called climbers. For example grape vines, money plant. The ones which spread on the ground are called creepers or runners. For example gourd plants.
Long Answer
41
Differentiate between taproot and fibrous root.
Answer
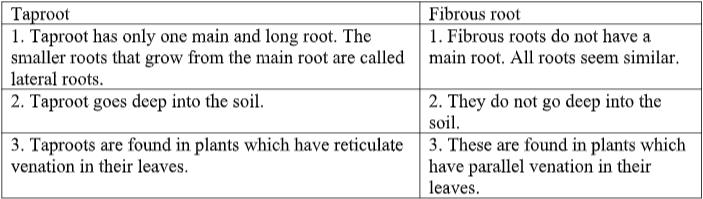
Long Answer
42
How are camels adapted to live in desert?
Answer
• The feet of the camels have thick, flat large soles which help them in the movement on sand.• The long legs of camel help in keeping the body away from the heat of the sand.
• They can live without water for a long time. When water is available, it drinks large amount of water at a time.
• They release very little urine to prevent loss of water.
Long Answer
43
What do you mean by leaf venation? Explain various types of leaf venation with example.
Answer
Leaf venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation. There are the following two types of leaf venation:(i) Reticulate venation: If the design of veins makes a net-like structure on both the sides of midrib then it is called reticulate venation. For example, mango leaf, gram leaf.
(ii) Parallel venation: If the veins are parallel to each other or to midrib then such type of venation is called parallel venation. For example, wheat leaf, barley.
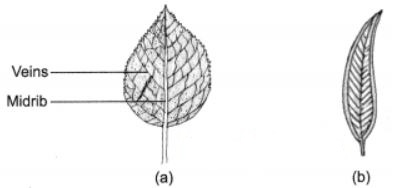
Long Answer
44
Identify the following plants as herbs, shrubs and trees.
(i) tomato
(ii) rice
(iii) eucalyptus
(iv) blueberry
(v) China rose
(vi) lavender
(vii) mango
(i) tomato
(ii) rice
(iii) eucalyptus
(iv) blueberry
(v) China rose
(vi) lavender
(vii) mango
Answer
(i) tomato – herb(ii) rice – herb
(iii) eucalyptus – tree
(iv) blueberry – shrub
(v) China rose – shrub
(vi) lavender – herb
(vii) mango – tree
Long Answer
45
How are camels living in hot desert differ from the camels living in cold desert?
Answer

Long Answer