SAQ for Chapter 5 The Rise of Empires Class 7 Social Science NCERT
Book Solutions1
Q1: Why was trade important for building and maintaining an empire?
Answer
Trade brought in money through taxes and allowed empires to afford large armies, roads, and ships. It also helped people get goods from faraway places and made cities grow richer.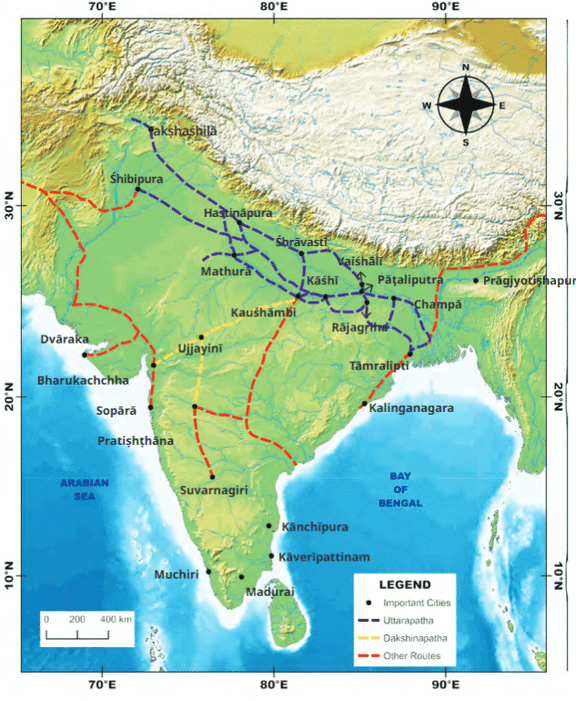
Trade Routes
SAQ
2
Q2: How did guilds (shrenis) support trade and society in ancient India?
Answer
Guilds helped traders and craftsmen work together, share resources, and support each other. They had their own rules and leaders and were often free from king’s control as long as trade flourished.
SAQ
3
Q3: What made Magadha a powerful kingdom before becoming an empire?
Answer
Magadha had fertile land, forests, rivers, and iron resources. These helped it grow crops, build weapons, and transport goods easily, making it a strong base for empire-building.
SAQ
4
Q4: How did the use of iron help in the growth of empires like Magadha?
Answer
Iron tools increased food production, and iron weapons made armies stronger. This allowed rulers to conquer more land and support growing populations.
SAQ
5
Q5: What happened when Alexander the Great invaded India?
Answer
Alexander fought and defeated King Porus but faced strong resistance. His soldiers refused to go further, and many died on the way back through deserts.
SAQ
6
Q6: How did the meeting between Alexander and Indian sages show cultural exchange?
Answer
Alexander met Indian sages called Gymnosophists, who impressed him with their wisdom. This meeting showed that ideas and philosophies were shared between cultures.
SAQ
7
Q7: What role did Megasthenes play in documenting the Mauryan Empire?
Answer
Megasthenes was a Greek ambassador in Chandragupta’s court. He wrote about India in his book Indika, describing cities, trade, and administration.
Megasthenes in the court of Chandragupta Maurya
SAQ
8
Q8: Why did Chandragupta Maurya choose Pataliputra as his capital?
Answer
Pataliputra was located near rivers and trade routes. It had rich land, strong defenses, and was ideal for administration and expansion.
SAQ
9
Q9: How did Kauṭilya help Chandragupta Maurya become emperor?
Answer
Kauṭilya used his knowledge of politics and economics to plan strategies. He supported Chandragupta in defeating the Nandas and uniting northern India.
SAQ
10
Q10: What kind of government system did the Mauryas have?
Answer
The Mauryas had a centralized government with strict laws and a strong administration. Officials collected taxes, maintained order, and ensured people’s welfare.
SAQ
11
Q11: How did Aśhoka spread Buddhism beyond India?
Answer
After the Kalinga War, Aśhoka sent messengers to Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia. He promoted Buddhist values of peace and kindness across Asia.
SAQ
12
Q12: What were Aśhoka’s contributions to public welfare?
Answer
Aśhoka built rest houses, planted trees, and provided medical care. He banned hunting and sent officials to check on people’s well-being.
SAQ
13
Q13: How did the Nanda dynasty contribute to the rise of the Maurya Empire?
Answer
The Nanda dynasty helped consolidate the region of Magadha, making it an ideal base for Chandragupta Maurya to rise to power and expand the empire.
SAQ
14
Q14: What was the role of Kauṭilya in the formation of the Maurya Empire?
Answer
Kauṭilya, also known as Chanakya, provided strategic advice, helped overthrow the Nandas, and guided Chandragupta in establishing and expanding the Maurya Empire.
SAQ
15
Q15: How did the Maurya Empire impact trade and administration?
Answer
The Mauryas built a strong administrative system and protected trade routes, facilitating economic growth, especially in trade and cities.
SAQ
16
Q16: What were Ashoka’s views on governance, as seen in his edicts?
Answer
Ashoka promoted moral governance based on dharma, emphasizing non-violence, justice, and the welfare of his people.
SAQ
17
Q17: Why was the Kalinga War significant for Ashoka’s rule?
Answer
The Kalinga War caused massive destruction, leading Ashoka to adopt Buddhism and promote peace, non-violence, and welfare through his edicts.
SAQ