NCERT Solutions for Chapter 5 Security in the Contemporary World Class 12 Political Science
Book Solutions1

Answer

2
(a) The spread of chikungunya / dengue fever
(b) Inflow of workers from a neighbouring nation
(c) Emergence of a group demanding nationhood for their region
(d) Emergence of a group demanding autonomy for their region
(e) A newspaper that is critical of the armed forces in the country
Answer
(a) Non-traditional(b) Non-traditional
(c) Traditional
(d) Not a threat
(e) Not a threat
3
Answer
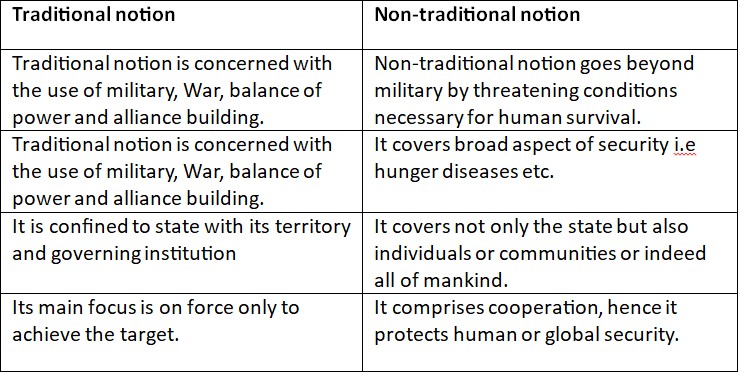
The creation and sustenance of alliance is related to the component of traditional security.
4
Answer
• Third World countries faced the prospect of military conflicts with neighbouring countries.• They also faced internal threats.
• Third World countries feared more from their neighbours than from Soviet Union or America.
• Internally, new states worried about threats from separatist movements which wanted to form independent countries.
5
Answer
Terrorism is a non-traditional threat to security. Terrorism is a new danger to individuals and human existence. It has emerged at the end of the 20th century. Terrorism refers to political violence that targets civilians deliberately and indiscriminately. Civilians are usually terrorised to act as a weapon against national governments and other parties in conflict. The classical examples of terrorism involve hijacking planes or planting bombs in trains, cafes, markets.6
Answer
In response to a threat of war, a government has three choices to do:• To surrender before the aggressor.
• To prevent the state from attacking by promising to raise the costs of war to an unacceptable level.
• To defend itself when there is actually a war.
7
Answer
Balance of power, in international relations, is the posture and policy of a nation or group of nations protecting itself against another nation or group by matching its power against the power of the other side.
A smaller country is always suspicious that war may break out with a bigger or more powerful country. Hence, they maintain a balance of power by building up military, economic, and technological power to protect their own security.
8
Answer
The objectives of military alliances:
• Military alliances are coalitions of states that coordinate their actions to deter or defend against military attack.
• Most alliances are formalised in written treaties and are based on a fairly clear identification of who constitutes the threat.
• Countries form alliances to increase their effective power relative to another country or alliance.
Example: The US backed Islamic militants in Afghanistan against the Soviet Union in the 1980s, but later attacked them when Al Qaeda, a group of Islamic militants led by Osama bin Laden, launched terrorist strikes against America on 11 September 2001.
9
Answer
Yes, rapid environmental degradation is causing a serious threat to security. Pollution, in whatever form, impacts how we live. Environmental deterioration poses a significant security risk. The pollution level in the air increases daily, as do global warming and depletion of the ozone layer—major environmental concerns needing immediate world response. For example, the Maldives may feel threatened by global warming because large parts of its territory may be submerged due to rising sea levels.10
Answer
The modern era is one of nuclear weapons. Nuclear weapons are extremely damaging and endanger humanity’s survival. The use of nuclear weapons or atomic explosives will have a global impact. Their usage—whether for prevention or ending war—has been reduced due to arms control methods of cooperation.
Nuclear weapons have limited usage due to arms-control cooperation. For example, the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968 regulates nuclear acquisition. Arms control regulates development/acquisition of weapons. The Anti-ballistic Missile (ABM) Treaty of 1972 sought to prevent the US and Soviet Union from using missiles as defence shields for attacks.
11
Answer
India has faced both traditional (military) and non-traditional threats from within and outside its borders. India’s security strategy depends on four broad components:
First, strengthening military capabilities, due to conflicts with neighbours.
Second, strengthening international norms and institutions to protect security interests.
Third, meeting internal security challenges.
Fourth, developing the economy so that citizens are lifted out of poverty and misery.
12

Answer
The cartoon depicts the relationship between conflict and terrorists. War is shown as fueling extremism. Connecting war with terror is often accurate because both are counterproductive. Terrorists intentionally and indiscriminately attack civilians, selecting civilian targets to terrorise the public and use discontent against governments or conflict parties.