NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8 Motion Class 9 Science
Book Solutions1
Answer
Yes, an object can have zero displacement even when it has moved through a distance.This happens when final position of the object coincides with its initial position. For example,if a person moves around park and stands on place from where he started then here displacement will be zero.2
Answer

Given, Side of the square field= 10m
Therefore, perimeter = 10 m × 4 = 40 m
Farmer moves along the boundary in 40s.
Displacement after 2 m 20 s = 2 × 60 s + 20 s = 140 s =?
Since in 40 s farmer moves 40 m
Therefore, in 1s distance covered by farmer = 40 / 40 m = 1m
Therefore, in 140s distance covered by farmer = 1 × 140 m = 140 m. Now, number of rotation to cover 140 along the boundary= Total Distance / Perimeter
= 140 m /40 m = 3.5 round
Thus, after 3.5 round farmer will at point C of the field.
Thus, after 2 min 20 seconds the displacement of farmer will be equal to 14.14 m north east from intial position.
3
Which of the following is true for displacement ?
(b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Answer
None of the statement is true for displacement First statement is false because displacement can be zero. Second statement is also false because displacement is less than or equal to the distance travelled by the object.1
Answer
|
Speed
|
Velocity
|
| Speed is the distance travelled by an object in a given interval of time. | Velocity is the displacement of an object in a given interval of time. |
| Speed = distance / time | Velocity = displacement / time |
| Speed is scalar quantity i.e. it has only magnitude. | Velocity is vector quantity i.e. it has both magnitude as well as direction. |
2
Answer
The magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed, only when an object is moving in a straight line.3
Answer
The odometer of an automobile measures the distance covered by an automobile.4
Answer
An object having uniform motion has a straight line path.5
Answer
Speed= 3 × 108 ms−1
Time= 5 min = 5 × 60 = 300 secs.
Distance= Speed × Time
Distance= 3 × 108 ms−1 × 300 secs. = 9 × 1010 m1
Answer
(i) A body is said to be in uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time.(ii) A body is said to be in nonuniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity is not constant.
2
Answer

3
Answer

1
Answer
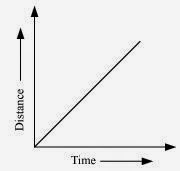
When the motion is uniform,the distance time graph is a straight line with a slope.
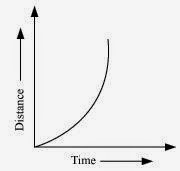
When the motion is non uniform, the distance time graph is not a straight line.It can be any curve.
2
Answer
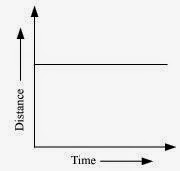
If distance time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis, the body is at rest.
3
What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer
If speed time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis, the object is moving uniformly.

4
Answer
The area below velocity-time graph gives the distance covered by the object.1
Answer
Initial speed of the bus, u= 0
Acceleration, a = 0.1 m/s2
Time taken, t = 2 minutes = 120 s
(a) v= u + at
v= 0 + 0.1 × 120
v= 12 ms–1
(b) According to the third equation of motion:
v2 - u2= 2as
Where, s is the distance covered by the bus
(12)2 - (0)2= 2(0.1) s
s = 720 m
Speed acquired by the bus is 12 m/s.
Distance travelled by the bus is 720 m.
2
Answer
Initial speed of the train, u= 90 km/h = 25 m/s
Final speed of the train, v = 0 (finally the train comes to rest)
Acceleration = - 0.5 m s-2
According to third equation of motion:
v2= u2+ 2 as
(0)2= (25)2+ 2 ( - 0.5) s
Where, s is the distance covered by the train![]()
3
Answer
Initial Velocity of trolley, u= 0 cms-1Acceleration, a= 2 cm s-2
Time, t= 3 s
We know that final velocity, v= u + at = 0 + 2 x 3 cms-1
Therefore, The velocity of train after 3 seconds = 6 cms-1
4
Answer
Initial Velocity of the car, u=0 ms-1Acceleration, a= 4 m s-2
Time, t= 10 s
We know Distance, s= ut + (1/2)at2
Therefore, Distance covered by car in 10 second= 0 × 10 + (1/2) × 4 × 102
= 0 + (1/2) × 4 × 10 × 10 m
= (1/2) × 400 m
= 200 m
5
Answer
Given Initial velocity of stone, u=5 m s-1
Downward of negative Acceleration, a= 10 m s-2
We know that 2 as= v2- u2

1
Answer
Diameter of circular track (D) = 200 m
Radius of circular track (r) = 200 / 2=100 m
Time taken by the athlete for one round (t) = 40 s
Distance covered by athlete in one round (s) = 2π r
= 2 × ( 22 / 7 ) × 100
Speed of the athlete (v) = Distance / Time
= (2 × 2200) / (7 × 40)
= 4400 / 7 × 40
Therefore, Distance covered in 140 s = Speed (s) × Time(t)
= 4400 / (7 × 40) × (2 × 60 + 20)
= 4400 / (7 × 40) × 140
= 4400 × 140 /7 × 40
= 2200 m
Number of round in 40 s =1 round
Number of round in 140 s =140/40
=3 1/2
After taking start from position X,the athlete will be at position Y after 3 1/2 rounds as shown in figure

Hence, Displacement of the athlete with respect to initial position at x= xy
= Diameter of circular track
= 200 m
2
Answer
Total Distance covered from AB = 300 m
Total time taken = 2 × 60 + 30 s
=150 s

Therefore, Average Speed from AB = Total Distance / Total Time
=300 / 150 m s-1
=2 m s-1
Therefore, Velocity from AB =Displacement AB / Time = 300 / 150 m s-1
=2 m s-1
Total Distance covered from AC =AB + BC
=300 + 200 m
Total time taken from A to C = Time taken for AB + Time taken for BC
= (2 × 60+30)+60 s
= 210 s
Therefore, Average Speed from AC = Total Distance /Total Time
= 400 /210 m s-1
= 1.904 m s-1
Displacement (S) from A to C = AB - BC
= 300-100 m
= 200 m
Time (t) taken for displacement from AC = 210 s
Therefore, Velocity from AC = Displacement (s) / Time(t)
= 200 / 210 m s-1
= 0.952 m s-1
3
Answer
The distance Abdul commutes while driving from Home to School = SLet us assume time taken by Abdul to commutes this distance = t1
Distance Abdul commutes while driving from School to Home = S
Let us assume time taken by Abdul to commutes this distance = t2
Average speed from home to school v1av = 20 km h-1
Average speed from school to home v2av = 30 km h-1
Also we know Time taken form Home to School t1 =S / v1av
Similarly Time taken form School to Home t2 =S/v2av
Total distance from home to school and backward = 2 S
Total time taken from home to school and backward (T) = S/20+ S/30
Therefore, Average speed (Vav) for covering total distance (2S) = Total Distance/Total Time
= 2S / (S/20 +S/30)
= 2S / [(30S+20S)/600]
= 1200S / 50S
= 24 kmh-1
4
Answer
Given Initial velocity of motorboat, u = 0Acceleration of motorboat, a = 3.0 m s-2
Time under consideration, t = 8.0 s
We know that Distance, s = ut + (1/2)at2
Therefore, The distance travel by motorboat = 0 ×8 + (1/2)3.0 × 82
= (1/2) × 3 × 8 × 8 m
= 96 m
5
Answer
As given in the figure below PR and SQ are the Speed-time graph for given two cars with initial speeds 52 kmh−1 and 3 kmh−1 respectively.

Distance Travelled by first car before coming to rest =Area of △ OPR
= (1/2) × OR × OP
= (1/2) × 5s × 52 kmh−1
= (1/2) × 5 × (52 × 1000) / 3600) m
= (1/2) × 5 × (130 / 9) m
= 325 / 9 m
= 36.11 m
Distance Travelled by second car before coming to rest =Area of △ OSQ
= (1/2) × OQ × OS
= (1/2) × 10 s × 3 kmh−1
= (1/2) × 10 × (3 × 1000) / 3600) m
= (1/2) × 10 x (5/6) m
= 5 × (5/6) m
= 25/6 m
= 4.16 m
6
Fig 8.11 shows the distance-time graph of three objects A, B and C. Study the graph and answer the following questions:
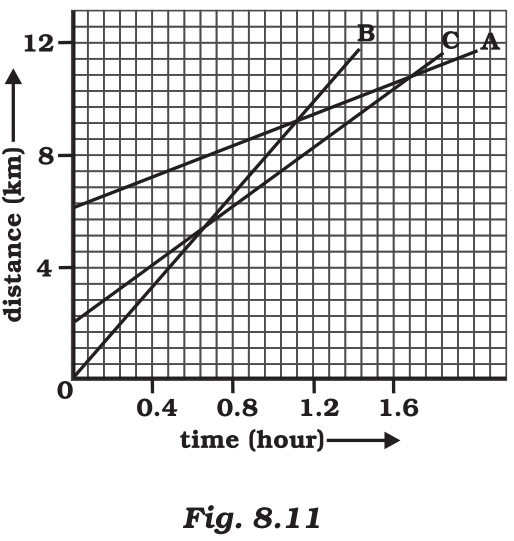
(a) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
(b) Are all three ever at the same point on the road?
(c) How far has C travelled when B passes A?
(d)How far has B travelled by the time it passes C?
Answer
(a) Object B
(b) No
(c) 5.714 km
(d) 5.143 km

Therefore, Speed = slope of the graph
Since slope of object B is greater than objects A and C, it is travelling the fastest.
(b) All three objects A, B and C never meet at a single point. Thus, they were never at the same point on road.
(c)

7 square box = 4 km
∴ 1 square box = 4/7 km
C is 4 blocks away from origin therefore initial distance of C from origin = 16/7 km
Distance of C from origin when B passes A = 8 km
Thus, Distance travelled by C when B passes A = 8 - 16/7
= (56 - 16)/7
= 40/7
= 5.714 km
(d)

Distance travelled by B by the time it passes C = 9 square boxes
9×4/7
= 36/7
= 5.143 km
7
Answer
Let us assume, the final velocity with which ball will strike the ground be 'v' and time it takes to strike the ground be 't'Initial Velocity of ball, u =0
Distance or height of fall, s =20 m
Downward acceleration, a =10 m s-2
As we know, 2as =v2-u2
v2 = 2as+ u2
= 2 x 10 x 20 + 0
= 400
∴ Final velocity of ball, v = 20 ms-1
t = (v-u)/a
∴Time taken by the ball to strike = (20-0)/10
= 20/10
= 2 seconds
8
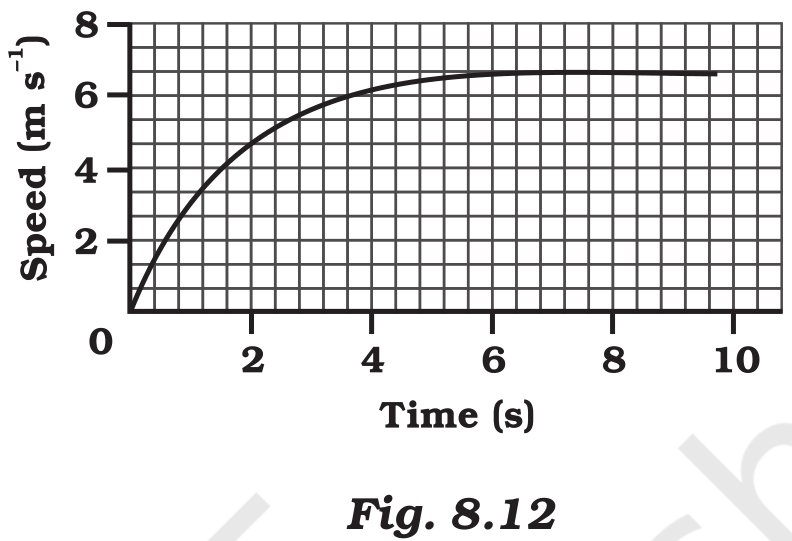
(a) Find out how far the car travels in the first 4 seconds. Shade the area on the graph that represents the distance travelled by the car during the period.
(b) Which part of the graph represents uniform motion of the car?
Answer

The shaded area which is equal to 1/2 × 4 × 6 = 12 m represents the distance travelled by the car in the first 4 s.
(b)

The part of the graph in red colour between time 6 s to 10 s represents uniform motion of the car.
9
(a) an object with a constant acceleration but with zero velocity.
(b) an object moving in a certain direction with an acceleration in the perpendicular direction
Answer
(a) PossibleWhen a ball is thrown up at maximum height, it has zero velocity, although it will have constant acceleration due to gravity, which is equal to 9.8 m/s2.
(b) Possible
When a car is moving in a circular track, its acceleration is perpendicular to its direction.
10
Answer
Radius of the circular orbit, r = 42250 kmTime taken to revolve around the earth, t= 24 h
Speed of a circular moving object, v = (2π r)/t
= [2× (22/7)×42250 × 1000] / (24 × 60 × 60)
= (2×22×42250×1000) / (7 ×24 × 60 × 60) ms-1
= 3073.74 ms-1