NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9 Maths
Book Solutions1
(Take the cost of a notebook to be x and that of a pen to be y).
Answer
Let the cost of a notebook = ₹ xThe cost of a pen = ₹ y
According to the condition,
we have [Cost of a notebook] = 2 x [Cost of a pen]
i.e. [x] = 2 x [y]
or
x = 2y
or
x – 2y = 0
Thus, the required linear equation is x – 2y = 0.
2(i)
2x + 3y =9.3
Answer
We have 2x + 3y = 9.3∴ (2)x + (3)y + (–9.3) = 0
Comparing it with ax + bx + c = 0,
we have a = 2, b = 3 and c = –9.3.
2(ii)
x – (y/5) – 10 = 0
Answer
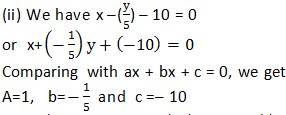
Note: Above equation can also be compared by:
Multiplying throughout by 5,
or 5(x) + (–1)y + (–50) = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0,
we get a = 5, b = –1 and c = –50.
2(iii)
–2x + 3y = 6
Answer
We have –2x + 3y = 6⇒ –2x + 3y – 6 = 0
⇒ (–2)x + (3)y + (–6) = 0
Comparing with ax + bx + c = 0,
we get a = –2, b = 3 and c = –6.
2(iv)
x = 3y
Answer
We have x = 3y⇒ x – 3y = 0
⇒ (1)x + (–3)y + 0 = 0
Comparing with ax + bx + c = 0,
we get a = 1, b = –3 and c = 0.
2(v)
2x = –5y
Answer
We have 2x = –5y⇒ 2x + 5y = 0
⇒ (2)x + (5)y + 0 = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0,
we get a = 2, b = 5 and c = 0.
2(vi)
3x + 2 = 0
Answer
We have 3x + 2 = 0⇒ 3x + 2 + 0y = 0
⇒ (3)x + (0)y + (2) = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0,
we get a = 3, b = 0 and c = 2.
2(vii)
y – 2 = 0
Answer
We have y – 2 = 0⇒ (0)x + (1)y + (–2) = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0,
we have a = 0, b = 1 and c = –2.
2(viii)
5 = 2x
Answer
We have 5 = 2x⇒ 5 – 2x = 0
⇒ –2x + 0y + 5 = 0
⇒ (–2)x + (0)y + (5) = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0,
we get a = –2, b = 0 and c = 5.
1
(i) a unique solution,
(ii) only two solutions,
(iii) infinitely many solutions
Answer
Option (iii) is true because a linear equation has an infinitely many solutions.2
(i) 2x + y = 7
(ii) πx + y = 9
(iii) x = 4y
Answer
(i) 2x + y = 7
When x = 0, 2(0) + y = 7
⇒ 0 + y = 7
⇒ y= 7
∴ Solution is (0, 7).
When x = 1, 2(1) + y = 7
⇒ y = 7 – 2
⇒ y= 5
∴ Solution is (1, 5).
When x = 2, 2(2) + y = 7
⇒ y = 7 – 4
⇒ y = 3
∴ Solution is (2, 3).
When x = 3 2(3) + y = 7 ⇒ y = 7 – 6
⇒ y = 1
∴ Solution is (3, 1).
(ii) πx + y = 9
When x = 0 π(0) + y = 9
⇒ y = 9 – 0
⇒ y= 9
∴ Solution is (0, 9).
When x = 1, π(1) + y = 9
⇒ y = 9 – π
∴ Solution is {1, (9 – π)}.
When x = 2 π(2) + y = 9
⇒ y = 9 – 2π
∴ Solution is {2, (9 – 2π)}.
When x = –1, p(–1) + y = 9
⇒ –π + y = 9
⇒ y = 9 + π
∴ Solution is {–1, (9 + π)}.
(iii) x = 4y When x = 0, 4y = 0
⇒ y = 0
∴ Solution is (0, 0).
When x = 1, 4y = 1
⇒ y = (1/4)
∴ Solution is (1, (1/4))
When x = 4, 4y = 4
⇒ y= (4/4) = 1
∴ Solution is (4, 1).
When x = –4, 4y = –4
⇒ y = (-4/4) = –1
∴ Solution is (–4, –1).
3
(i) (0, 2)
(ii) (2, 0)
(iii) (4, 0)
(iv) (√2, 4√2)
(v) (1, 1)
Answer
(i) (0, 2) means x = 0 and y = 2
Putting x = 0 and y = 2 in x – 2y = 4,
we have L.H.S. = 0 – 2(2) = –4
But R.H.S. = 4
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ x = 0, y = 0 is not a solution.
(ii) (2, 0) means x = 2 and y = 0
∴ Putting x = 2 and y = 0 in x – 2y = 4,
we get L.H.S. = 2 – 2(0) = 2 – 0 = 2
But R.H.S. = 4
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (2, 0) is not a solution.
(iii) (4, 0) means x = 4 and y = 0
Putting x = 4 and y = 0 in x – 2y = 4,
we get L.H.S. = 4 – 2(0) = 4 – 0 = 4
But R.H.S. = 4
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ (4, 0) is a solution.
(iv) (2 , 4√2) means x = 2 and y = 4√2
Putting x = 2 and y = 4√2 in x – 2y = 4,
we get L.H.S. =√2 – 2 ( 4√2) = √2 – 8√2
= √2(1 – 8) = –7√2
But R.H.S. = 4 ∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (√2, 4√2) is not a solution.
(v) (1, 1) means x = 1 and y = 1
Putting x = 1 and y = 1 in x – 2y = 4,
we get L.H.S. = 1 – 2(1) = 1 – 2 = –1
But R.H.S. = 4
⇒ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S
∴ (1, 1) is not a solution.
4
Answer
We have 2x + 3y = kPutting x = 2 and y = 1 in 2x + 3y = k,
we get 2(2) + 3(1) = k
⇒ 4 + 3 = k
⇒ 7 = k
Thus, the required value of k = 7.
1
(i) x + y = 4
(ii) x - y = 2
(iii) y = 3x
(iv) 3 = 2x + y
Answer
(i)x + y= 4
⇒ y = 4 – x
If we have x = 0,
then y = 4 – 0 = 4 x = 1,
then y = 4 – 1 = 3 x = 2,
then y = 4 – 2 = 2
∴ We get the following table:
|
x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
y |
4 |
3 |
2 |
Plot the ordered pairs (0, 4), (1, 3) and (2, 2) on the graph paper. Joining these points, we get a line AB as shown below.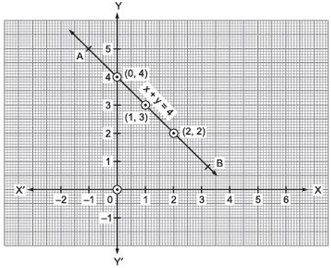
Thus, the line AB is the required graph of x + y = 4.
(ii) x – y = 2
⇒ y = x – 2
If we have x = 0,
then y = 0 – 2 = –2 x = 1,
then y = 1 – 2 = – 1 x = 2,
then y = 2 – 2 = 0
∴ We have the following table:
|
x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
y |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
Plot the ordered pairs (0, –2), (1, –1) and (2, 0) on the graph paper. Joining these points, we get a straight line PQ as shown below: Thus, the line PQ is required graph of x – y = 2.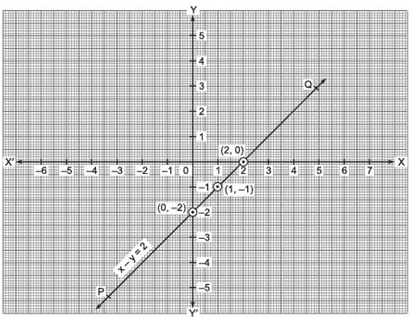
(iii) y = 3x
If x = 0, then y = 3(0)
⇒ y = 0 x = 1, then y = 3(1)
⇒ y = 3 x = –1, then y = 3(–1)
⇒ y = –3
∴ We get the following table:
|
x |
0 |
1 |
-1 |
|
y |
0 |
3 |
-3 |
Plot the ordered pairs (0, 0), (1, 3) and (–1, –3) on the graph paper. Joining these points, we get the straight line LM.
Thus, LM is the required graph of y = 3x.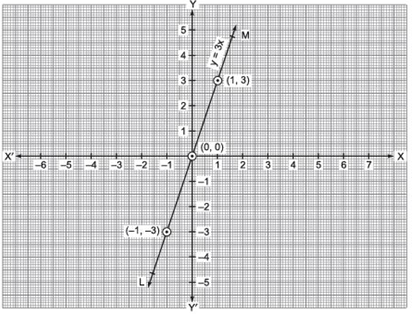
Note: The graph of the equation of the form y = kx is a straight line which always passes through the origin.
( iv) 3 = 2x + y
⇒ y = 3 – 2x
∴ If x = 0, then y = 3 – 2(0)
⇒ y = 3 If x = 1, then y = 3 – 2(1)
⇒ y = 1 If x = 2, then y = 3 – (2)
⇒ y = –1
|
x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
y |
3 |
1 |
-1 |
Plot the ordered pairs (0, 3), (1, 1) and (2, –1) on the graph paper. Joining these points, we get a line CD.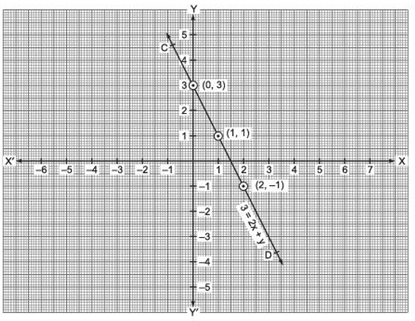
Thus, the line CD is the required graph of 3 = 2x + y
2
Answer
(2, 14) means x = 2 and y = 14Following equations can have (2, 14) as the solution, i.e. they can pass through the point (2, 14).
(i) x + y = 16
(ii) 7x – y = 0
There can be an unlimited number of lines which can pass through the point (2, 14) because an unlimited number of lines can pass through a point.
3
Answer
The equation of the given line is 3y = ax + 7∵ (3, 4) lies on the given line.
∴ It must satisfy the equation 3y = ax + 7
We have (3, 4)
⇒ x = 3 and y = 4
L.H.S. = 3y
= 3 x 4
= 12
R.H.S. = ax + 7
= a x 3 + 7
= 3a + 7
∵ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ 12 = 3a + 7
or
3a = 12 – 7 = 5
or
a = (5/3)
Thus, the required value of a is (5/3).
4
For the first kilometre, the fare is ₹ 8 and for the subsequent distance it is ₹ 5 per km. Taking the distance covered as x km and total fare as ₹ y, write a linear equation for this information and draw its graph.
Answer
Here, total distance covered = x km
Total taxi fare = ₹ y
Fare for the 1st km = ₹ 8
Remaining distance = (x – 1) km
∴ Fare for (x – 1) km = ₹ 5 x (x – 1) km
Total taxi fare = ₹ 8 + ₹ 5(x – 1)
∴ According to the condition,
y = 8 + 5(x – 1)
⇒ y = 8 + 5x – 5
⇒ y = 5x + 3
which is the required linear equation representing the given information.
Graph: We have y = 5x + 3
∴ When x = 0, y = 5(0) + 3
⇒ y = 3
When x = –1, y = 5(–1) + 3
⇒ y = –2
When x = –2, y = 5(–2) + 3
⇒ y = –7
∴ We get the following table:
|
x |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
|
y |
3 |
-2 |
-7 |
Now, plotting the ordered pairs (0, 3), (–1, –2) and (–2, –7) on a graph paper and joining them, we get a straight line PQ.
Thus, PQ is the required graph of the linear equation y = 5x + 3.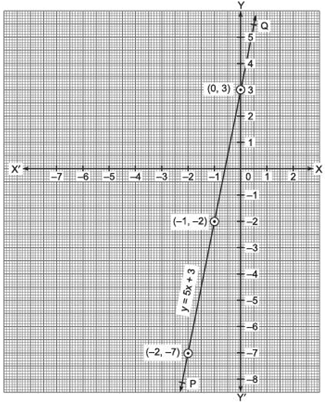
5
From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graphs are given in Fig. (i) and Fig.(ii).
|
For Fig. (i) |
For Fig. (ii) |
|
(i) y = x |
(i) y = x + 2 |
|
(ii) x + y = 0 |
(ii) y = x – 2 |
|
(iii) y = 2x |
(iii) y = –x + 2 |
|
(iv) 2 + 3y = 7x |
(iv) x + 2y = 6 |
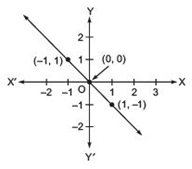
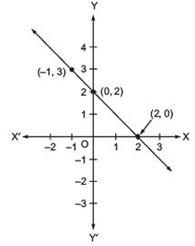
Answer
For Fig. (i), the correct linear equation is x + y = 0
[∵ (–1, 1) ⇒ –1 + 1 = 0 and (1, –1)
⇒ 1 + (–1) = 0]
For Fig. (ii), the correct linear equation is y = –x + 2
[∵ (–1, 3) ⇒ 3 = –(–1) + 2 ⇒ 3 = 3 and (0, 2)
⇒ 2 = –(0) + 2 ⇒ 2 = 2]
6
(i) 2 units (ii) 0 unit
Answer
Constant force is 5 units.
Let the distance travelled = x units and work done = y units.
Since, Work done = Force x Displacement
⇒ y= 5 × X
⇒ y= 5x
Drawing the graph
We have y = 5x
When x = 0, then y = 5(0) = 0
When x = 1, then y = 5(1) = 5
When x = 1.5, then y = 5(1.5) = 7.5
∴ We get the following table:
|
x |
0 |
1 |
1.5 |
|
y |
0 |
5 |
7.5 |
Plotting the ordered pairs (0, 0), (1, 5) and (1.5, 7.5) on the graph paper and joining the points, we get a straight line OB.
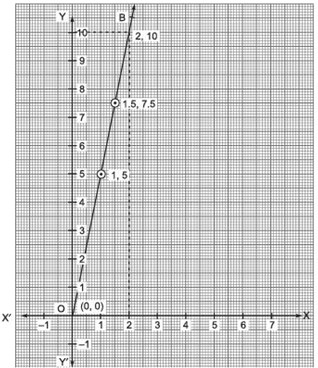
From the graph, we get
(i) Distance travelled = 2 units
∴ x = 2, then y = 10 units
⇒ Work done = 10 units.
(ii) Distance travelled = 0 units
∴ y = 5x
⇒ y = 5(0) = 0
∴ Work done = 0 unit.
7
Answer
Let the contribution of Yamini = ₹ x and the contribution of Fatima = ₹ y
∴ We have x + y = 100
⇒ y = 100 – x
Now, when x = 0, y = 100 – 0 = 100
When x = 50, y = 100 – 50 = 50
When x = 100, y = 100 – 100 = 0
We get the following table:
|
x |
0 |
50 |
100 |
|
y |
100 |
50 |
0 |
For drawing the graph, plot the ordered pairs (0, 100), (50, 50) and (100, 0) on a graph paper.
Joining these points we get a line PQ.
Thus, PQ is the required graph of x + y = 100.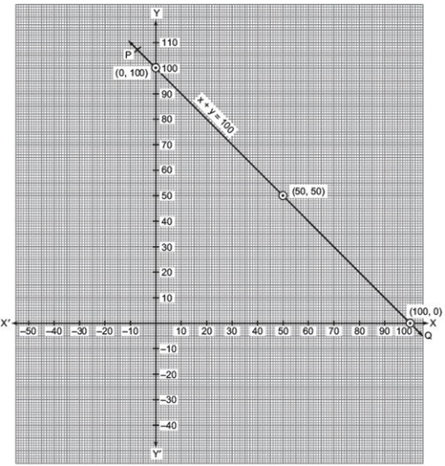
8
F= (9/5)C + 32
(i) Draw the graph of the linear equation above using Celsius for x-axis and Fahrenheit for y-axis.
(ii) If the temperature is 30ºC, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit?
(iii) If the temperature is 95ºF, what is the temperature in Celsius?
(iv) If the temperature is 0ºC, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit and if the temperature is 0ºF, what is the temperature in Celsius?
(v) Is there a temperature which is numerically the same in both Fahrenheit and Celsius? If yes, find it.
Answer
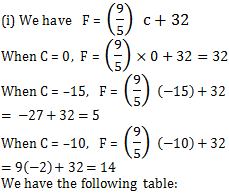
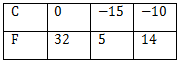
Plot the ordered pairs (0, 32), (–15, 5) and (–10, 14) on a graph paper. Joining these points we get a straight line AB.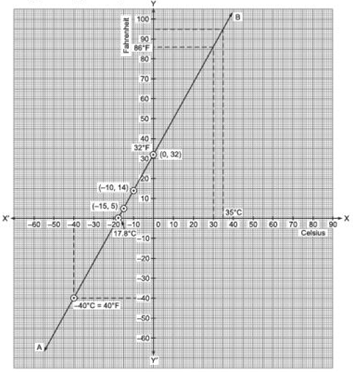
(ii) From the graph, we have
86ºF corresponds to 30ºC
(iii) From the graph, we have
95ºF = 35ºC
(iv) From the graph, we have
0ºC = 32ºF
and 0ºF = 17.8ºC
(v) Yes, from the graph, we have
40ºF = –40ºC
1
(i) in one variable
(ii) in two variables
Answer
(i) y = 3 [An equation in one variable]
∵ y = 3 is an equation in one variable, i.e. y only.
∴ It has a unique solution y = 3 as shown on the number line shown here.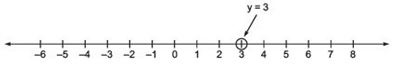
The unique solution is a point.
(ii) y = 3 [An equation in two variables]
We can write y = 3 as
0.x + y = 3
Now, when x = 1, y = 3
when x = 2, y = 3
when x = 3, y = 3
We get the following table: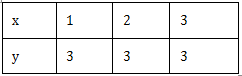
Plotting the ordered pairs (1, 3), (2, 3) and (3, 3) on a graph paper, we get a line AB as solution of 0 . x + y = 3, i.e. y = 3.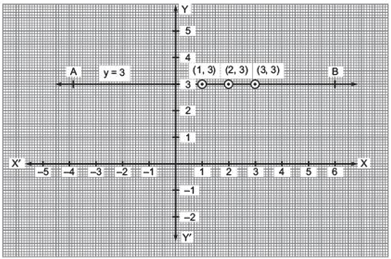
2
(i) in one variable
(ii) in two variables
Answer
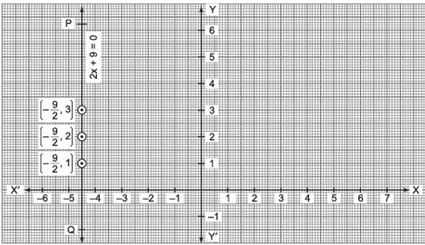
(i) 2x + 9 = 0 [An equation in one variable]
We have: 2x + 9 = 0
⇒ 2x = –9
⇒ x = (-9/2)
which is a linear equation in one variable ‘x’ only. Its solution is the point (-9/2) on the number line as shown below.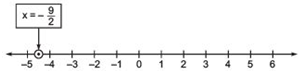
(ii) 2x + 9 = 0 [An equation in two variables]
We can write 2x + 9 = 0 as 2x + 0y + 9 = 0 or 2x = –9 + 0y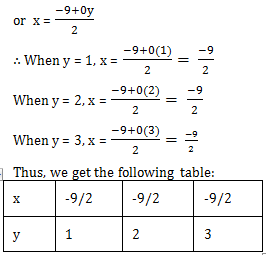
Now, plotting the ordered pairs ![]() on a graph paper and joining them, we get a line PQ as solution of 2x + 9 = 0.
on a graph paper and joining them, we get a line PQ as solution of 2x + 9 = 0.