NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Is Matter around us Pure? Class 9 Science
Book Solutions1
Answer
A material that is composed of only one type of particles is called pure substance. All the constituent particles of a pure substance have same chemical nature.2
Answer
|
Homogeneous mixtures
|
Heterogeneous mixtures
|
| Homogeneous mixtures have uniform composition. | Heterogeneous mixtures have non uniform composition. |
| It has no visible boundaries of separation between its constituents. | It has visible boundaries of separation between its constituents. |
1
Answer
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture having a uniform composition throughout the mixture. For example, mixtures of salt in water, sugar in water, copper sulphate in water, iodine in alcohol, alloy, and air have uniform compositions throughout the mixtures.On the other hand, a heterogeneous mixture is a mixture having a non-uniform composition throughout the mixture. For example, composition of mixtures of sodium chloride and iron fillings, salt and sulphur, oil and water, chalk powder in water, wheat flour in water, milk and water are not uniform throughout the mixtures.
2
Answer
|
Sol
|
Solution
|
Suspension
|
| They are heterogeneous in nature. | They are homogeneous in nature. | They are heterogeneous in nature. |
| They scatter a beam of light and hence show Tyndall effect. | They do not scatter a beam of light and hence do not show Tyndall effect | They scatter a beam of light and hence show Tyndall effect. |
| They are quite stable. | Examples of solution are: salt in water, sugar in water. | Examples of suspension are: sand in water, dusty air |
3
Answer
Mass of solute (sodium chloride) = 36 g (Given)
Mass of solvent (water) = 100 g (Given)
Then, mass of solution = Mass of solute + Mass of solvent
= (36 + 100) g
= 136 g
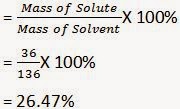
1
Answer
Kerosene and petrol are miscible liquids also the difference between their boiling point is more than 25 ºC so they can be separated by the method of distillation. 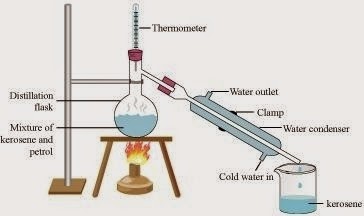
In this method, the mixture of kerosene and petrol is taken in a distillation flask with a thermometer fitted in it. We also need a beaker, a water condenser, and a Bunsen burner. The apparatus is arranged as shown in the above figure. Then, the mixture is heated slowly. The thermometer should be watched simultaneously. Kerosene will vaporize and condense in the water condenser. The condensed kerosene is collected from the condenser outlet, whereas petrol is left behind in the distillation flask.
2
Answer
(i) By Centrifugation
(ii) By Evaporation
(iii) By Sublimation
3
Answer
The crystallisation method is used to purify solids.1
• Cutting of trees
• Melting of butter in a pan
• Rusting of almirah
• Boiling of water to form steam
• Passing of electric current through water, and water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gas
• Dissolving common salt in water
• Making a fruit salad with raw fruits
• Burning of paper and wood
Answer
• Physical change
• Physical change
• Chemical change
• Physical change
• Chemical change
• Physical change
• Physical change
• Chemical change
2
Answer
1
Answer
2
Answer
First, water is taken as a solvent in a saucer pan. This water (solvent) is allowed to boil. During heating, milk and tea leaves are added to the solvent as solutes. They form a solution. Then, the solution is poured through a strainer. The insoluble part of the solution remains on the strainer as residue. Sugar added to the filtrate, which dissolves in the filtrate. The resulting solution is the required tea.3
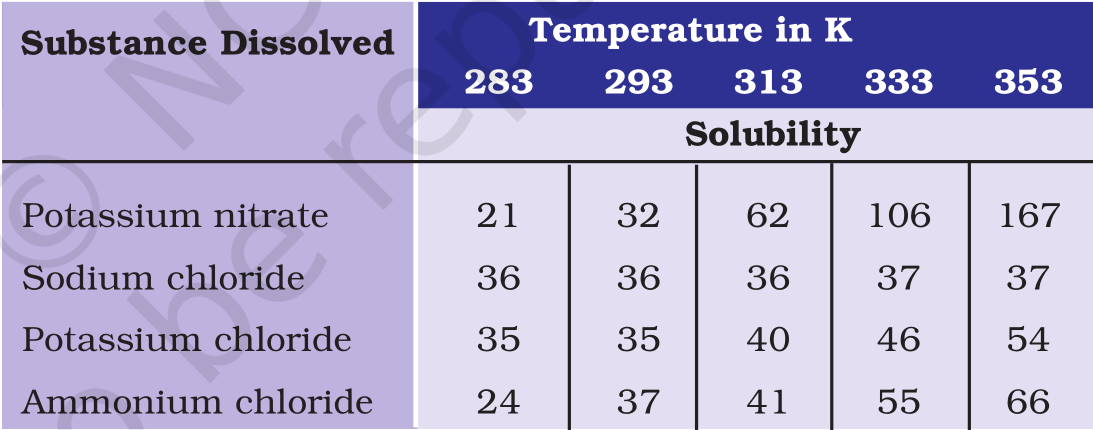
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. What salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
Answer
(a) Since 62 g of potassium nitrate is dissolved in 100g of water to prepare a saturated solution at 313 K, 31 g of potassium nitrate should be dissolved in 50 g of water to prepare a saturated solution at 313 K.
(b) The amount of potassium chloride that should be dissolved in water to make a saturated solution increases with temperature. Thus, as the solution cools some of the potassium chloride will precipitate out of the solution.
(c) The solubility of the salts at 293 K are:
Potassium nitrate – 32 g
Sodium chloride – 36 g
Potassium chloride – 35 g
Ammonium chloride – 37 g
Ammonium chloride has the highest solubility at 293 K.
(d) The solubility of a salt increases with temperature.
4
(a) Saturated solution
(b) Pure substance
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension
Answer
(a) Solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a particular temperature is known as saturated solution. For example in aqueous solution of sugar no more sugar can be dissolved at room temperature.(b) A pure substance is a substance consisting of a single type of particles i.e., all constituent particles of the substance have the same chemical properties. For example water, sugar, salt etc.
(c) A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture whose particles are not as small as solution but they are so small that cannot be seen by naked eye. When a beam of light is passed through a colloid then the path of the light becomes visible. For example milk, smoke etc.
(d) A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solids are dispersed in liquids. The solute particles in suspension do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the medium. For example Paints, Muddy water chalk water mixtures etc.
5
Soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea
Answer
Homogeneous mixtures: Soda water, air, vinegar, filtered teaHeterogeneous mixtures: Wood, soil
Note: Pure air is homogeneous mixture but Polluted air is heterogeneous mixture.
6
Answer
Take a sample of colourless liquid and put on stove if it starts boiling exactly at 100 ºC then it is pure water. Any other colourless liquid such as vinegar always have different boiling point. Also observe carefully that after some time whole liquid will convert into vapour without leaving any residue.7
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric Acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air
Answer
The following materials fall in the category of a "pure substance":(a) Ice
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
8
(a) Soil
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water
Answer
The following mixtures are solutions:(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(e) Soda water
9
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution
Answer
Tyndall effect is shown by colloidal solution. Here, milk and starch solution are colloids therefore milk and starch solution will show Tyndall effect.10
(a) Sodium
(b) Soil
(c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver
(e) Calcium carbonate
(f) Tin
(g) Silicon
(h) Coal
(i) Air
(j) Soap
(k) Methane
(l) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Answer
Elements: Sodium, Silver, Tin and Silicon.
Compounds: Calcium carbonate, Methane and carbon dioxide.
Mixtures: Soil, Sugar, Coal, Air, Soap and Blood.
11
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron fillings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of candle
Answer