NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Science
Book Solutions1
Answer
2
Answer
1
Answer
Pentane has three structural isomers. They are: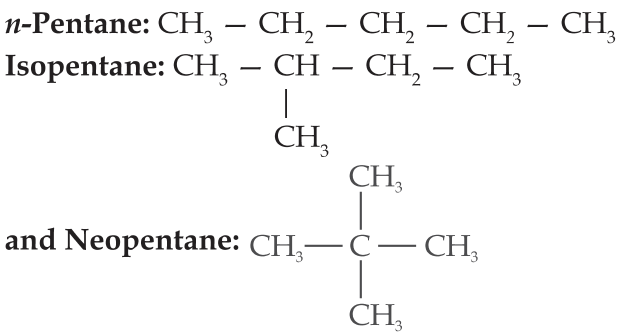
2
Answer
The two features of carbon that give rise to a large number of compounds are as follows:→ Catenation: It is the ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.
→ Tetravalency: With the valency of four, carbon is capable of bonding with four other atoms.
3
Answer
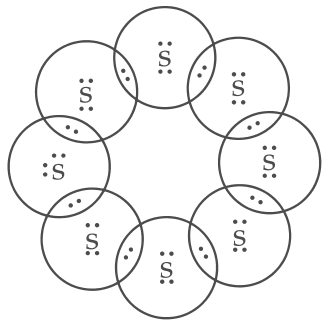
The formula for cyclopentane is C5H10. Its electron dot structure is given below.
4
(ii) Bromopentane*
(iii) Butanone
Answer
(i) Ethanoic acid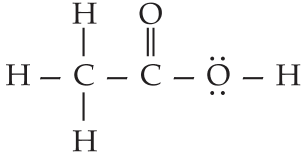
(ii) Bromopentane: There are three structural isomers possible for bromopentane.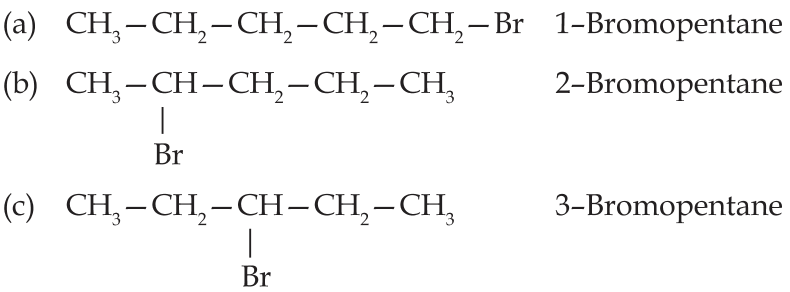
(iii) Butanone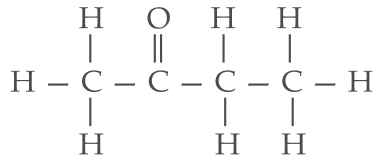
(iv) Hexanal
![]()
5
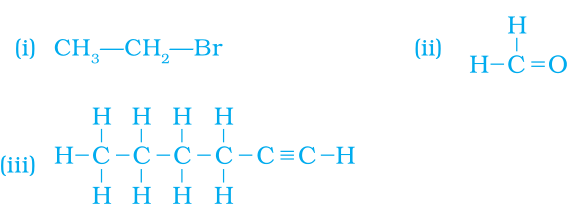
Answer
(i) Bromoethane or 1-Bromoethane(ii) Methanal (formaldehyde)
(iii) Hexyne or Hex-1-yne
1
Answer
CH3CH2OH + (Alkaline KMnO4) → CH3COOHSince, in this reaction one oxygen is added to ethanol, hence it is an oxidation reaction.
2
Answer
2HC ≡ CH + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O + HeatWhen ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame. This is due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of air. However, if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame with temperature 3000°C because of complete combustion. This oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is not possible to attain such a high temperature without mixing oxygen. This is the reason why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
1
Answer
Litmus test: Treat the given compound with blue litmus solutions. If the blue litmus solution turns red, it is a carboxylic acid and if does not turn red, it is an alcohol.
Carbonate and Hydrogen Carbonate Test: We can distinguish between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of their reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Acid reacts with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate to evolve CO2 gas that turns lime water milky.
2
Answer
Oxidising agents are the substances that gain electrons in redox reaction and whose oxidation number is reduced.1
Answer
Detergent gives lather with hard and soft water both, while a soap gives lather with soft water only. Thus, it is not possible to check if water is hard; by using a detergent.2
Answer
A soap molecule has two parts namely hydrophobic and hydrophilic. With the help of these, it attaches to the grease or dirt particle and forms a cluster called micelle. These micelles remain suspended as a colloid. To remove these micelles, it is necessary to agitate clothes.1
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
Answer
(b) 7 covalent bonds.2
(a) carboxylic acid.
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone.
(d) alcohol.
Answer
(c) ketone.3
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.4
Answer
The structure of CH3Cl is given below: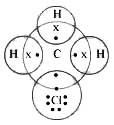
Carbon has four valence electrons. It shares 1 electron each with 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 electron with chlorine. The bond between C and Cl atoms is covalent but due to higher value of electro-negativity of Cl, the C–Cl bond is polar in nature.
5
(a) ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) propanone.
(d) F2.
Answer
(a) Structure of ethanoic acid: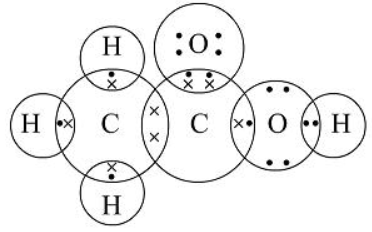
(b) Structure of H2S:![]()
(c) Structure of propanone: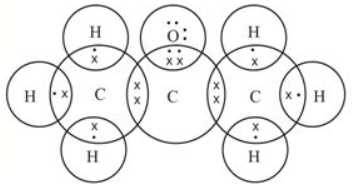
(d) Structure of F2:![]()
6
Answer
A homologous series is a series of carbon compounds that have different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional group.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of -CH2 unit between each successive compound.
7
Answer
Ethanol and Ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their following properties:
→ Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant smell. Ethanoic acid has a melting point of 17°C. Since it is below the room temperature so, it freezes during winter. Moreover, ethanoic acid has a smell like vinegar.
→ Ethanol does not react with metal carbonates while, ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide. For example,
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
→ Ethanol does not react with NaOH while ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH to form sodium ethanoate and water. For example,
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O→ Ethanol is oxidized to give ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4 while, no reaction takes place with ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4.
8
Answer
9
Answer
Carbon and its compounds give large amount of heat on combustion due to high percentage of carbon and hydrogen. Carbon compounds used as fuel have optimum ignition temperature with high calorific values and are easy to handle. Their combustion can e controlled. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.10
Answer
Hard water often contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Soap molecules react with the salts of calcium and magnesium and form a precipitate. This precipitate begins floating as an off-white layer over water. This layer is called scum. Soaps lose their cleansing property in hard water because of formation of scum.11
Answer
Since soap is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.12
Answer
Hydrogenation is the chemical reaction between hydrogen and other compounds in the presence of catalyst. It is used mainly to reduce saturated hydrocarbons. Hydrogenation is an addition reaction.For Example: When ethene is heated with the catalyst nickel it is reduced to ethane.
Industrial application:
→ It is also used to prepare vegetable ghee from vegetable oils.
13
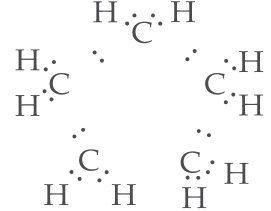
C2, H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.14
Answer
Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats (solids).15
Answer
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.